As more parents and caregivers try to create healthier boundaries around technology, many eventually reach the point where they want their child’s iPhone to feel helpful rather than chaotic, which is exactly why learning how to configure Apple’s parental control tools becomes one of the most valuable steps toward building a safe and predictable digital routine at home.
Because iPhones offer an enormous range of apps, games, videos, social features, and messaging options, children can easily become overwhelmed by choices or exposed to content they simply are not ready for, so setting up a thoughtful structure around usage allows families to avoid unnecessary stress while still letting kids enjoy the good parts of technology.
When adults guide this process slowly and intentionally, children tend to feel more secure because rules feel clear instead of confusing, and expectations stay consistent across school nights, weekends, and special situations.
Apple’s built-in parental controls, primarily managed through Screen Time, offer robust features without requiring technical knowledge, and once configured carefully, these tools help adults shape how the device is used, which apps remain available, what type of content can load, and how much total time is allowed each day. The goal is not surveillance; the goal is balanced, mindful use.
This guide is intentionally long and detailed, ensuring even first-time iPhone users can follow every step with confidence.
Part 1 — Understanding the Tools: What iPhone Parental Controls Actually Include
Before moving into the step-by-step instructions, it helps to develop a solid understanding of what Apple’s controls can do, because a clear overview allows families to decide which features they really need and which may not matter for their household.
iPhone parental controls include several major categories:
-
Downtime, which limits access to apps during certain hours so that evenings and nights stay calmer.
-
App Limits, creating time blocks for specific categories such as games, social apps, entertainment apps, or any individual app you want to control separately.
-
Always Allowed, which ensures essential tools like calls, messages, or maps remain accessible even during restricted periods.
-
Content & Privacy Restrictions, used to filter explicit material, block adult websites, prevent account changes, restrict purchases, and control what the child can install.
-
Purchase and Download Approval, which is available when using Family Sharing to require parental permission before a child installs or buys apps.
-
Communication Limits, keeping track of who the child can talk to during allowed hours or downtime.
-
Location features, which allow the parent to find the device or check location sharing settings.
-
Shared controls, allowing multiple caregivers to supervise the same child’s device through their own Apple IDs.
Understanding these tools early makes the configuration process feel smoother, since you can choose the sequence that best fits your family’s needs.
Part 2 — Preparing the iPhone for Parental Controls
Setting up Screen Time and restrictions becomes much easier once the foundational elements are in place. Therefore, the preparation phase includes everything from verifying Apple IDs to enabling Family Sharing, and it ensures that any limits you set later will apply correctly and consistently.
Step 1 — Make sure each person has an Apple ID
Children need their own Apple ID for parental controls to function smoothly.
-
Check whether your child already uses an Apple ID.
-
If not, create one for them directly from your device using Family Sharing.
-
Use accurate age information, since Apple adjusts restrictions accordingly.
-
Add a recovery option so the account can be recovered if the child forgets a password.
Step 2 — Turn on Family Sharing
Family Sharing connects your devices and makes parental controls far easier to manage.
-
Open Settings on your iPhone.
-
Tap your name at the top of the screen.
-
Choose Family Sharing.
-
Add your child to your family group.
-
Confirm your role as the organizer or guardian.
-
Accept any prompts that allow supervision and Screen Time management.
Once these steps are completed, your device becomes capable of managing the child’s iPhone remotely, which helps reduce confusion.
Part 3 — Setting Up Screen Time for the Child’s iPhone
Screen Time is the central hub for all parental controls on iPhone, so the next section explains exactly how to enable and configure it.
Step 1 — Activate Screen Time
-
Go to Settings on the child’s iPhone.
-
Scroll to Screen Time.
-
Tap “Turn On Screen Time.”
-
Choose “This is My Child’s iPhone.”
-
Follow the introductory prompts that explain each feature.
A key part of this process is creating a Screen Time passcode, which ensures the child cannot modify restrictions. Pick a code the child does not know but you will not forget.
Step 2 — Set Downtime to create calm periods
Downtime helps families create predictable routines by limiting non-essential apps during evenings, late nights, or school hours.
You may:
-
Choose a nightly start time when entertainment shuts off.
-
Create a morning end time when apps become available again.
-
Adjust the schedule for weekends or special events.
Downtime works best when explained gently to your child, so they understand it’s meant to support rest, not to punish.
Step 3 — Add App Limits for categories or individual apps
App Limits allow families to balance fun and responsibilities.
You may set:
-
A daily limit for games.
-
A separate limit for social apps.
-
A short cap for entertainment apps.
-
Individual limits for any specific app that tends to cause distraction.
The strength of App Limits lies in their flexibility, because you can update them whenever you want without needing to unlock the child’s device physically.
Step 4 — Choose which apps are Always Allowed
This section helps you keep essential tools accessible even during restrictions.
Commonly always allowed apps include:
-
Phone
-
Messages
-
Maps
-
Camera
-
A school-related app
-
A health or emergency tool
Setting this up ensures your child can always reach you.
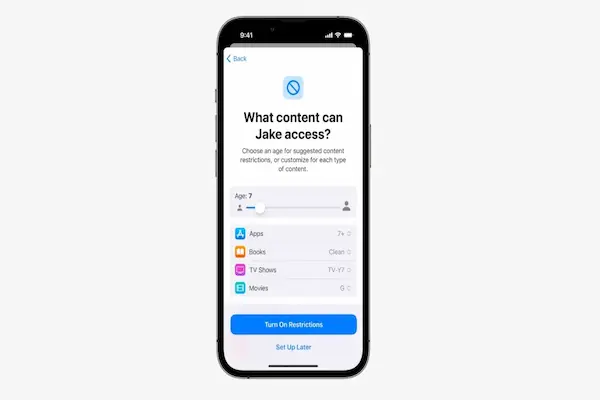
Part 4 — Configuring Content & Privacy Restrictions
Content & Privacy Restrictions form the protective layer that keeps inappropriate or unsafe actions from occurring, so it is important to spend enough time reviewing each option.
1. Content Restrictions
You can manage what the child sees across various apps and stores.
Controls include:
-
Restricting explicit music or podcasts
-
Limiting movies and TV shows by age rating
-
Filtering adult website content in Safari
-
Blocking explicit language in Siri requests
-
Preventing web content that exceeds the allowed maturity level
These options work together to create a healthier environment for browsing and media.
2. Privacy Controls
Privacy controls help manage sensitive device permissions.
You can limit or approve:
-
Location sharing
-
Microphone access
-
Camera usage
-
Contacts access
-
Photos access
-
Bluetooth connections
-
Advertising tracking preferences
Explaining these settings to your child builds trust, because they understand what information stays private.
3. Allowed App Permissions
Here you can disable system features entirely if needed.
You may turn off:
-
Installing apps
-
Deleting apps
-
In-app purchases
-
Account changes
-
Cellular data changes
-
Passcode changes
Each of these prevents accidental or intentional changes that might affect safety or the phone’s behavior.
Part 5 — App Store and Purchase Restrictions
Accidental purchases are common among younger users, so Apple allows strong control over what a child may buy or download.
Using Ask to Buy
When Ask to Buy is enabled:
-
Every download request alerts the parent.
-
You may approve or deny instantly from your device.
-
No app, game, book, or subscription is added without permission.
Blocking purchases entirely
You may completely disable:
-
App Store downloads
-
In-app purchases
-
Subscription sign-ups
This ensures financial safety and reduces surprises.
Part 6 — Communication Limits for Your Child’s Safety
Apple includes communication restrictions to support safer interactions.
You can restrict:
-
Who the child can message during allowed hours
-
Who the child can communicate with during downtime
-
Whether unknown contacts can initiate conversations
-
Whether communication syncing across devices is permitted
These features are particularly helpful for younger children who are still learning digital boundaries.
Part 7 — A Step-by-Step Example Setup for a Typical Family
Because seeing an example often makes the process easier, here is a long-form sample configuration that a busy caregiver might set for a child aged 10–13.
1. Downtime
-
Weeknights: 8:00 PM until 7:00 AM
-
Weekends: 9:00 PM until 8:00 AM
-
All apps except calls and messages paused
2. App Limits
-
Games: 1 hour per day
-
Social apps: 30 minutes per day
-
YouTube or entertainment apps: 45 minutes per day
-
Educational apps: no limits
-
Browser: allowed with content filters
3. Always Allowed
-
Phone
-
Messages
-
Maps
-
A family communication app
-
A school app
4. Content Restrictions
-
Web content filtered
-
No explicit music, videos, or books
-
Age-appropriate ratings only
-
Safe search enabled
5. Privacy Restrictions
-
Limited location access
-
Camera allowed
-
Microphone allowed
-
Photos access restricted to selected apps
-
Contacts allowed for essential apps only
6. Purchase Controls
-
Ask to Buy enabled
-
No in-app purchases
-
No subscription sign-ups without approval
Once configured, the device supports healthy digital behavior without requiring constant nagging.
Part 8 — Talking With Your Child About Digital Rules
Because controls are only part of the solution, families benefit from honest, calm discussions that explain why rules exist. Children respond better when routines feel collaborative rather than imposed suddenly.
Helpful conversation ideas:
-
Explain that restrictions exist to protect—not punish.
-
Share your own digital habits to show that balance applies to everyone.
-
Ask how screens make your child feel, especially before bedtime.
-
Discuss safe communication practices.
-
Encourage breaks and screen-free activities.
-
Invite your child to suggest limits that feel fair.
A short family agreement may cover:
-
When phones can be used
-
When phones stay outside the bedroom
-
Which apps need permission
-
How homework and screen time work together
-
What happens if rules are ignored
Clear expectations reduce conflict dramatically.
Part 9 — A Monthly Digital Checkup to Keep Things Running Smoothly
Even well-set parental controls need occasional review.
Use this long checklist once per month:
-
Review app usage reports for unexpected changes.
-
Adjust Downtime hours as school or sleep needs shift.
-
Add or remove App Limits based on current routines.
-
Confirm Ask to Buy is still active.
-
Check storage space for photos and apps.
-
Review contacts and communication limits.
-
Update content restrictions as the child matures.
-
Test the Screen Time passcode to ensure you still remember it.
-
Confirm the device is backed up properly.
-
Talk with your child about how the rules feel.
Regular reviews prevent surprises.
FAQs for Caregivers Setting iPhone Parental Controls
1. Can children turn off Screen Time?
Not if you keep the Screen Time passcode private. Without it, changes cannot be made.
2. Will these controls read my child’s messages?
No. Apple does not give access to message content through Screen Time.
3. Do parental controls stop cyberbullying?
Controls help limit exposure and manage communication, but family conversations remain essential.
4. Can both parents manage Screen Time?
Yes, if both are added to Family Sharing as guardians.
5. What happens if my child forgets their Apple ID password?
Because the account belongs to a child in Family Sharing, adults can help reset it.
Conclusion: A Calmer Digital Experience Starts With Clear Structure
Although modern devices can feel overwhelming for families trying to encourage healthy habits, iPhone’s parental control system allows adults to create a flexible digital environment where safety and independence can grow together. When Screen Time and restrictions are configured with care, children experience fewer distractions, clearer routines, and safer boundaries, while adults gain confidence knowing the device supports—not disrupts—family life.